DISCOVER
THE WONDERS OF
CHINESE SOLAR
TERMS
Agricultural production is closely related to geographical and climatic resources. Superior geographical and climatic resources are essential for the birth of agricultural civilization. China is located in the eastern part of the Eurasian continent and the west coast of the Pacific Ocean. There are considerable differences in thermal properties between land and sea, resulting in the most typical monsoon climate in the world. Monsoon climate is a mixture of continental climate and oceanic climate. In winter, affected by the dry and cold airflow from the inland, the weather is cold, dry, and rainy; in summer, affected by the warm and moist airflow from the ocean, the weather is high, humid, and rainy. Sufficient sunshine, abundant precipitation, high temperatures, and humid rain and heat are China's very superior climate resources. The high-temperature period coincides with the rainy period, and a good combination of water and heat is very beneficial to the growth of crops. Climatic elements include light, temperature, and precipitation, among which precipitation is an important element of climate. The 24 solar terms accurately reflect the changing laws of natural rhythms and played an extremely important role in ancient agricultural production.
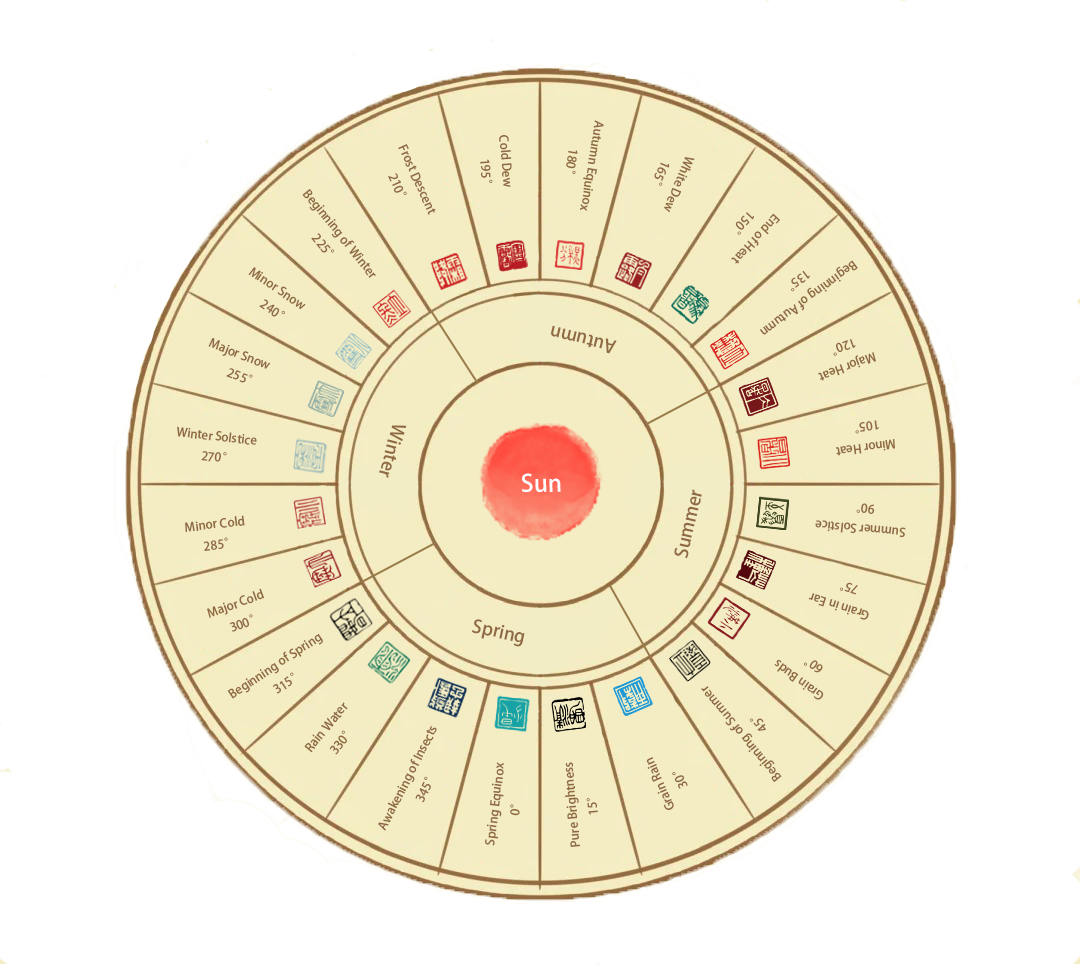
The "24 Solar Terms" is a product of ancient farming civilization. It is a knowledge system formed by ancient ancestors who followed the farming season, observed the movement of celestial bodies, and understood the changing laws of seasons, climate, phenology, etc., during the year. 24 solar terms were initially formulated based on the movement of the stars. The Big Dipper rotates in cycles, and one rotation of the handle clockwise is a cycle called "year" (photography). The current "24 solar terms" are based on the sun's return to the ecliptic. The sun's position is formulated by dividing the annual motion trajectory of the sun into 24 equal parts, with every 15° being an equal part and every equal part being a solar term. One year, four seasons, three months each in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, each month has two solar terms, each with its unique meaning.

Spring


Summer


Autumn


Winter